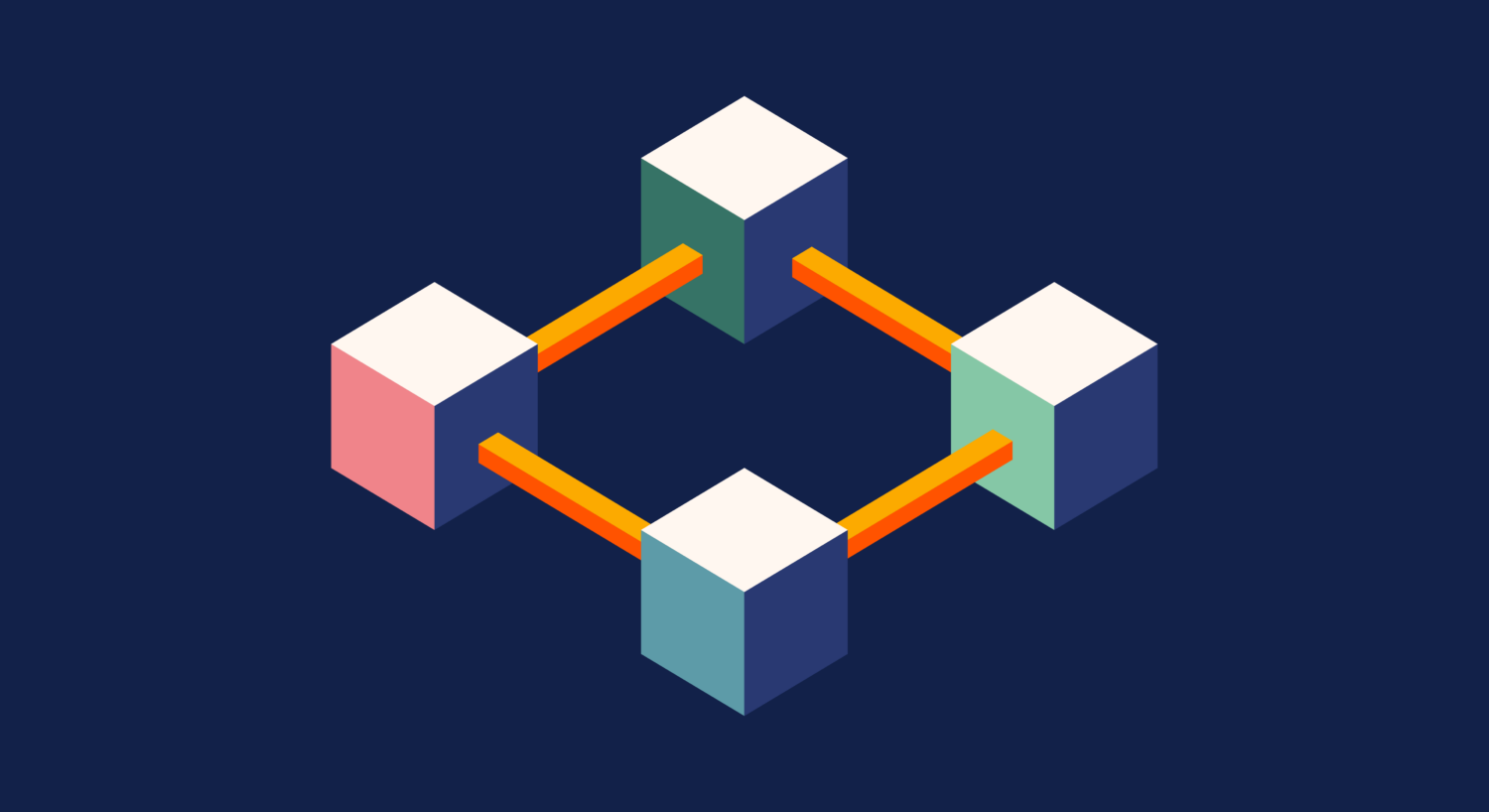
Blockchain : Why is it getting more and more popular?
Over the past decade, the term "Blockchain" has come to our ears very often. But a very few people (all the tech geeks out there) know what is it exactly.
 |
| Fig. 1- A Blockchain |
In simple terms, Blockchain is a technology that enables the secure sharing of information. Despite it being known widely for its impenetrability, the idea behind Blockchain is quite simple.
A blockchain is a type of distributed database or ledger which means the power to update a blockchain is distributed between the nodes, or participants, of a public or private computer network. This is known as Distributed Ledger Technology, or DLT.
What is Blockchain?
Like the name suggests, a blockchain is basically a chain of blocks. A Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is completely open to anyone. It is very secure as once any data has been recorded inside a blockchain, it gets very difficult to change it.
How does a Blockchain work?
 |
| Fig. 2- A 'Block' |
A more detailed look inside a 'block' can help us understand how this works.
Each 'block' of a Blockchain contains some data, the hash of the block and the hash of the previous block. The data stored inside a block depends on the type of the blockchain. For example, a block of Bitcoin contains the details about a transaction like the sender, the receiver and the number of coins.
The hash of a block is like its fingerprint. It identifies the block and is unique for every block. Changing something inside the block will cause the hash to change. So, if the hash of a block changes, you get to know that there have been some changes inside the block.
The third element of a block is the hash of the previous block. It is this connection that makes a Blockchain so secure.
The History of Blockchain
This technique was originally described in 1991 and was intended to timestamp digital documents so that it is not possible to backdate them or tamper with them. However, this technology remained unused until the development of the cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, in 2009.
Is Blockchain as secure as it is said to be?
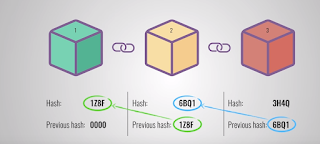 |
| Fig. 3- A valid Blockchain. |
The security of a Blockchain depends on its system of blocks. For example, if the data in the second block is changed, its hash changes. This makes all the following blocks invalid as the following blockchain still have the old hash in them. This disrupts or breaks a blockchain and makes it invalid.
But this is only the first layer of security. Nowadays, computers have become very fast and can calculate hundreds of thousands of hashes in a second so you can easily tamper with a block and recalculate the hashes of all the other blocks to make the blockchain valid again.
 |
| Fig. 4- An invalid Blockchain |
So, to mitigate this, Blockchains have something called Proof-of-Work. It slows down the process of making a new block. In the case of Bitcoin, it takes about 10 minutes to calculate the proof of work and add a new block to the chain. This makes it very hard to tamper with the blocks because after tampering with one block, you need to recalculate the Proof-of-Work for all the following blocks. So, basically the security of a Blockchain comes from the creative use of hashes and proof-of-work.
Another way Blockchains stay secure is by distributing themselves. Instead of using a central entity to manage themselves, they use a peer to peer network and anyone is allowed to join. When someone joins the network, they get a full copy of the Blockchain. This can be used by the node to verify if everything is in order.
When a new block is made, it is sent to everyone on the network and the node verifies the block to make sure it hasn't been tampered with. If everything goes well, each node adds the block to its Blockchain. Blocks that are tampered will be rejected by other nodes.
So, to successfully tamper with a Blockchain, you will have to tamper all the blocks on the chain, redo the proof-of-work and take control of 50% of the peer to peer network. Only then your block will be accepted by the other nodes. This is almost impossible to do.
All of these features make Blockchains very secure and almost impossible to tamper with or hack.
These are the basic functions and security features of Blockchains. For more interesting info about technology, follow this blog.
Give any suggestions or reviews by dropping a comment below.
Thank you
Aarav Iyer
References:
(1) Youtube (Figs. 2, 3 and 4 + Content)
(2) Wikipedia (Fig. 1 + Content)
(3) McKinsey and Company

